The Australia migration shift 2026 marks a significant change in how the country manages skilled workers, international students, and temporary migrants. From July 1, 2026, Australia is implementing a redesigned migration strategy focused on skills shortages, sustainable population growth, and better workforce planning. These changes are guided by federal migration planning levels and administered through Australia’s immigration authorities under updated policy frameworks released during 2025. The shift responds to record-high net overseas migration figures, labour shortages in critical sectors, and housing and infrastructure pressures. With revised visa categories, new salary thresholds, and clearer pathways to permanent residency, Australia’s migration system in 2026 is more targeted than in previous years.
Australia has traditionally relied on migration to support economic growth, but recent surges in temporary arrivals prompted a reassessment of priorities. The new approach aims to reduce short-term churn while increasing long-term contributions to the economy.
This article explains the Australian migration changes 2026, who is affected, and how the new system reshapes opportunities for migrants and employers.
What Is Driving Australia’s Migration Shift in 2026?
The migration shift is driven by a combination of economic, social, and infrastructure pressures. Australia experienced unprecedented migration growth following border reopenings, largely due to international students and temporary visa holders.
The government’s response focuses on quality over quantity, prioritising skilled migrants who fill long-term workforce gaps while tightening settings for temporary entry.
Key Policy Changes Under Australia Migration Shift 2026
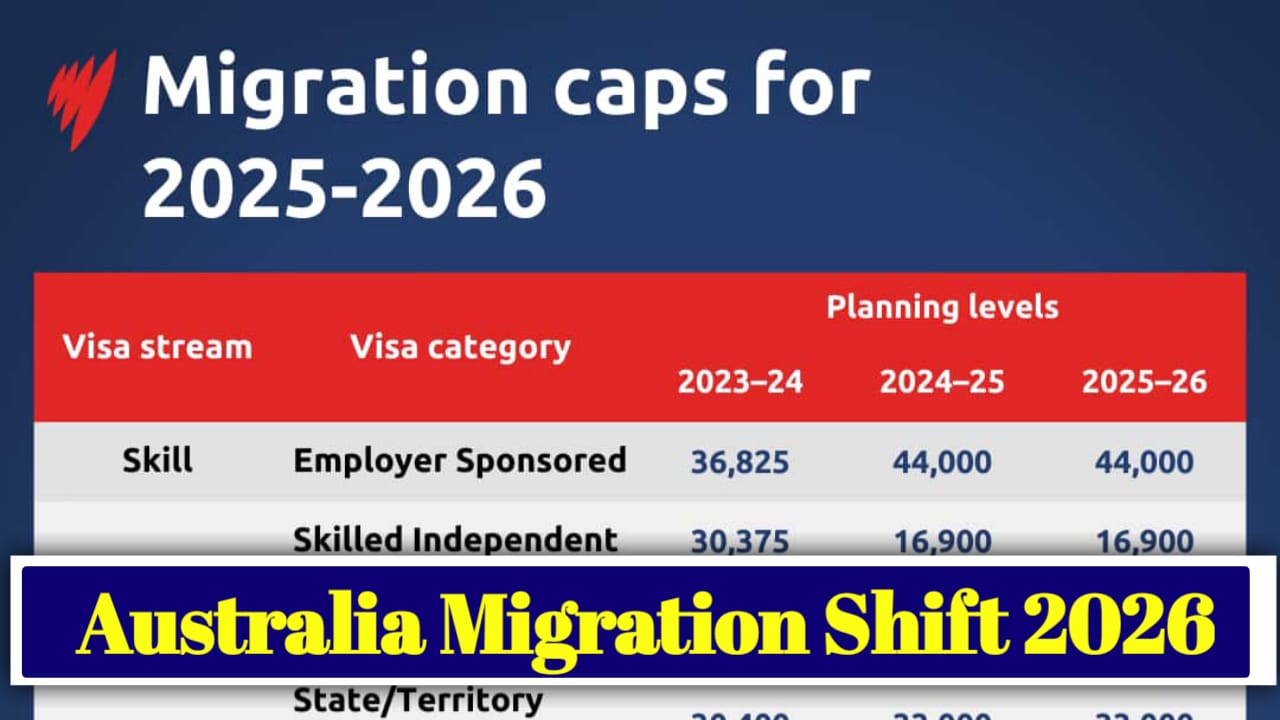
The Australia migration shift 2026 introduces structural reforms across student, skilled, and employer-sponsored visas. The goal is to align migration intake more closely with national needs.
| Policy Area | Previous Approach | 2026 Shift | Affected Group | Key Objective | Impact Level | Duration Focus | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skilled Migration | Broad intake | Targeted skills | Skilled workers | Fill shortages | High | Long-term | Priority sectors |
| Student Visas | High volume | Tighter settings | International students | Reduce churn | Moderate | Temporary | Better oversight |
| Salary Thresholds | Lower limits | Increased minimums | Sponsored workers | Fair wages | High | Ongoing | Market alignment |
| Employer Sponsorship | Complex pathways | Streamlined system | Employers | Faster hiring | High | Medium-term | Simplified visas |
| Temporary Migration | Growth-driven | Controlled intake | Temp visa holders | Stability | Moderate | Short-term | Reduced reliance |
| Permanent Residency | Fragmented routes | Clear pathways | Skilled migrants | Retention | High | Permanent | Predictability |
| Regional Migration | Limited incentives | Stronger focus | Regional areas | Workforce balance | Moderate | Long-term | Regional growth |
| Compliance Measures | Reactive | Proactive | All visa holders | Integrity | High | Continuous | Stronger monitoring |
ALSO READ-
Changes for International Students in 2026
International students remain important to Australia’s education sector, but the new strategy tightens entry and post-study settings. The focus is on genuine students and improved compliance.
• Stronger checks on education providers
• Reduced reliance on student-to-work visa hopping
Graduates with in-demand skills will still have pathways, but automatic transitions are reduced.
Skilled Visa Reforms and Workforce Priorities
The Australia skilled migration 2026 framework prioritises healthcare, construction, technology, and essential services. Visa processing is redesigned to be faster and more predictable for both migrants and employers.
Higher salary thresholds aim to prevent underpayment and ensure skilled migrants are genuinely filling high-value roles.
Employer-Sponsored Migration Changes
Employer-sponsored visas are being simplified into clearer streams. Businesses facing labour shortages benefit from faster approvals, but must meet stricter compliance and wage requirements.
This balances employer needs with worker protections and labour market integrity.
Impact on Temporary Migrants and Visa Holders
Temporary migrants will see fewer extensions and clearer time limits. The new system discourages long-term temporary stays without progression to permanent roles.
For migrants already in Australia, transition options depend on skills, earnings, and employer sponsorship.
Regional Migration and Population Balance
Regional Australia plays a larger role under the Australian migration policy 2026. Incentives encourage skilled migrants to settle outside major cities where labour shortages are more acute.
This supports regional economies while easing pressure on housing and services in urban centres.
What Migrants Should Prepare for in 2026
Prospective migrants should align qualifications and experience with priority occupation lists. Planning early and understanding revised eligibility rules is essential.
The shift rewards long-term contribution rather than short-term presence.
FAQs on Australia Migration Shift 2026
Q1. Does Australia migration shift 2026 reduce total migration numbers?
Yes, it aims to moderate growth while improving quality.
Q2. Are international students still welcome in Australia?
Yes, but with stricter rules and fewer automatic pathways.
Q3. Will skilled migrants have clearer PR pathways in 2026?
Yes, permanent residency pathways are more structured.
Conclusion
The Australia migration shift 2026 represents a decisive move toward a more strategic, skills-focused migration system. By tightening temporary visa settings and strengthening skilled and regional pathways, Australia aims to balance economic growth with social sustainability. Migrants who understand these changes and align with national priorities will be best positioned to succeed under the new framework.
